The visit of the faculty members of the Faculty of Physics to the National Observatory ...
Report of the scientific-specialist visit of physics faculty students to the applied nanotechnology industrialization center ...
Academic Calendar- Fall 2023
Report of the meeting of the Faculty of Physics with Rayan Roshdafzar company
The appointment of Dr. Hassan Beigi as the president of Kharazmi University
2023/09/20The visit of the faculty members of the Faculty of Physics to the National Observatory ...
2023/09/9Report of the scientific-specialist visit of physics faculty students to the applied nanotechnology industrialization center ...
2023/09/9Academic Calendar- Fall 2023
2023/09/9Report of the meeting of the Faculty of Physics with Rayan Roshdafzar company
2023/08/20The appointment of Dr. Hassan Beigi as the president of Kharazmi University
- About
- Academic
- News & events
- Apply to KHU
-
Laboratories
- ─── Research Labs ─────
- NanoPhotonic Lab
- BioPhotonic Lab
- OpticPhotonic Lab
- NanoPhotonic Sensors & OptoFluidics Lab
- Advanced Plasma Lab
- Medical Plasma Lab
- ─── Central Lab ────────
- Central Lab
- ─── Educational Labs ────
- SolidState Lab
- Physics1 Lab
- Physics2 Lab
- Physics3 Lab
- Physics4 Lab
- Optics Lab
- Advanced CondensedMatter Lab
- Advanced SolidState Lab
- ─── Research Intitutes ───────
- Research Institute of Applied Sciences
- Plasma Research Institute
- ────── WorkShops ────────
- Solar Oven Workshop
- Electrotechnical Workshop
- Announcements
- Education
- Research
Advanced Plasma Lab

Currently, the advanced plasma laboratory is equipped with suitable devices and power sources to create plasma at low pressure and atmospheric pressure.
1- Research fields of low pressure plasma
Plasma address layer by PVD plasma sputtering method
Chemical vapor deposition using PECVD plasma
Nitration and plasma carbonation
Synthesis of various catalysts using plasma
Creation of hydrophilic surfaces in the plasma environment
2- Plasma research fields at atmospheric pressure
Hydrophilicity of surfaces
The effect of plasma on plants and seeds
Removal of biological pollutants from water
Removal of organic pollutants from water
Plasma applications in oil and petrochemical industry
3- Study of dense plasma
Study of plasma produced by focal plasma device
1.1 Preparation for laboratory work
Before starting work in the laboratory, familiarize yourself with the following:
Hazards of materials in the laboratory as well as appropriate protocols for handling, storage and emergency measures. Read labels and safety data sheets (SDS) before handling or opening chemicals. Never use product from unlabeled containers and report missing labels to your supervisor.
Agents, processes and equipment available in the laboratory. If you are unsure about any aspect of a procedure, consult your lab supervisor before proceeding.
Locating and operating safety and emergency equipment such as fire extinguishers, eyewash stations and emergency showers, first aid and spill response kits, fire alarm stations, telephones and emergency exits.
Emergency spill response procedures for the materials you will be working with.
Emergency reporting methods and phone numbers.
Designated and alternative escape routes.
1.2 during laboratory work
Observe the following rules when working in the laboratory:
Restrict access to the lab to authorized persons only. Children are not allowed to enter the laboratory.
smoking, eating, drinking, holding food, drink or tobacco; The use of cosmetics and the use of contact lenses are not allowed in the laboratories.
Wear long lab coats and safety glasses in labs that use chemicals, biohazards, or radioisotopes. Open shoes, such as sandals, should never be worn in the laboratory.
Keep work areas clean and free of unwanted chemicals, biological samples, radioactive materials and unused equipment. Avoid leaving reagent bottles, empty or full, on the floor.
Work with materials only when you know their flammability, reactivity, toxicity, safe handling and storage, and emergency procedures.
Read safety data sheets before working with hazardous chemicals or infectious agents.
Never pipette by mouth. Use mechanical transmissions.
Walk, don't run, in the lab.
Keep exits and passages clear at all times.
Ensure that access to emergency equipment (eye wash stations, emergency showers and fire extinguishers) is not blocked.
Wash your hands thoroughly before leaving the laboratory.
Avoid using headphones.
1.3 Cleaning before departure
At the end of each test and before leaving the laboratory, do a safety check. be sure that:
Turn off gas, water, electricity, vacuum and pressure lines and heating and cooling devices
Return unused materials, equipment and devices to their proper storage location
Label, package and dispose of all waste materials properly
Remove defective or damaged equipment immediately and arrange for repair or replacement
Disinfect any equipment or work areas that may have come into contact with hazardous materials.
When leaving the laboratory, put aside the protective clothing (lab coat, gloves, etc.).
If you are the last person to leave the lab, close and lock the lab door
1.4 Regulations for working alone in the laboratory
Working alone is an unsafe practice at any time. However, if the nature of your work makes it unavoidable, take steps to ensure that others are aware of your location and that someone will visit you from time to time, either in person or on the phone.
Before doing anything alone in the lab, review this checklist to determine if it is appropriate to proceed:
Is your supervisor aware of your plans?
Are there dangerous experiments?
Examples: high temperature, high vacuum, highly flammable materials (low flash point), toxic materials
Have you reviewed your procedure with your supervisor?
Do you have a written operating procedure?
Are your devices and equipment in good working condition?
Are you trained to do the job?
Do you have a login/logout method?
Do you have an emergency?
Do you have access to a campus phone (rather than a cell phone) in case of an emergency?
Does your lab door have a viewing window or other means to indicate someone is inside?
Do you know the emergency evacuation method?
Do you have access to a phone in an emergency?
Do you have access to first aid supplies?
1. Atmospheric plasma jet of argon gas
A plasma jet at atmospheric pressure is a non-thermal plasma discharge that leads to the creation of a flux of highly active chemical particles. As a result of the impact of electrons, argon gas is excited and ionized. The plasma flux that moves at a high speed contains ions, electrons, highly active radicals that undergo a rapid recombination process.
Atmospheric plasma jet is discharge type with dielectric barrier. This jet works with a power source with radio frequency waves at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and a power range between 15 and 200 watts with argon gas flow. This fountain has two cylindrical coaxial electrodes that are separated from each other by quartz insulation and the gas passes between them.
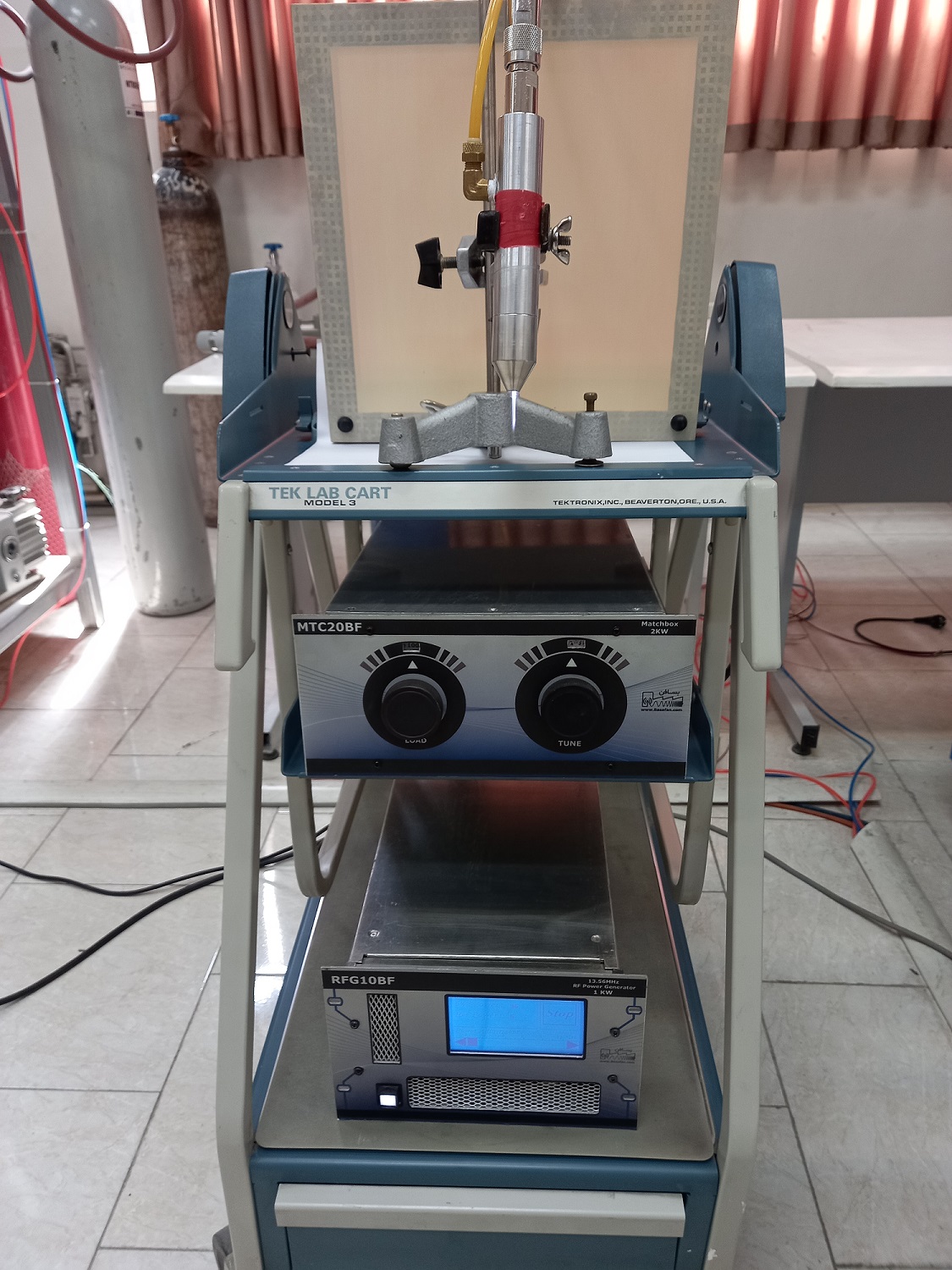


Plasma jet with power supply
applications:
Activation and cleaning of the surface of plastics or metals
Surface disinfection
Water activation
Removal of organic pollutants in water
Application in agriculture and medicine
So far, many students have completed their thesis on the interaction of this plasma with cancerous substances and cells, DNA and RNA.
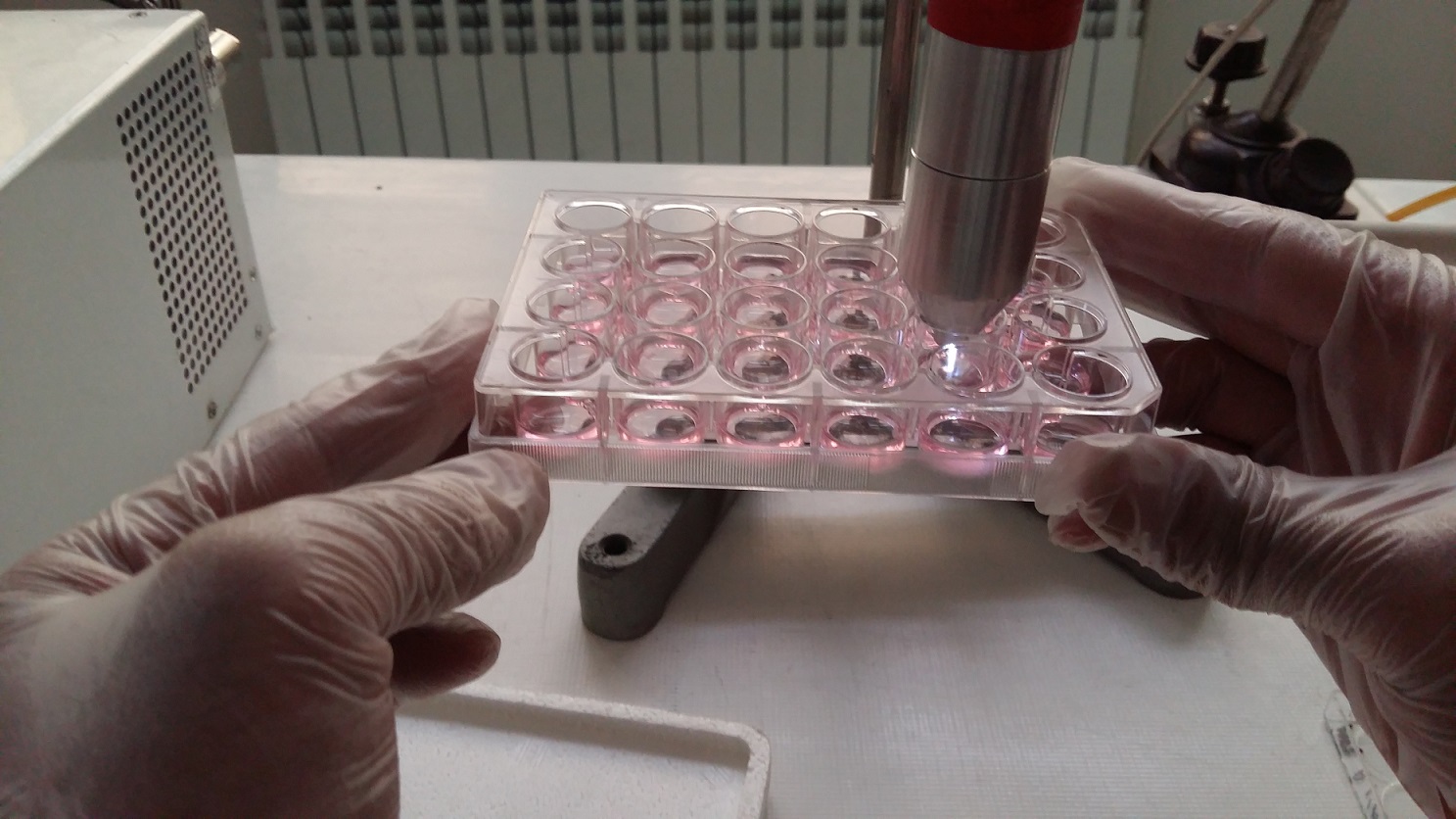
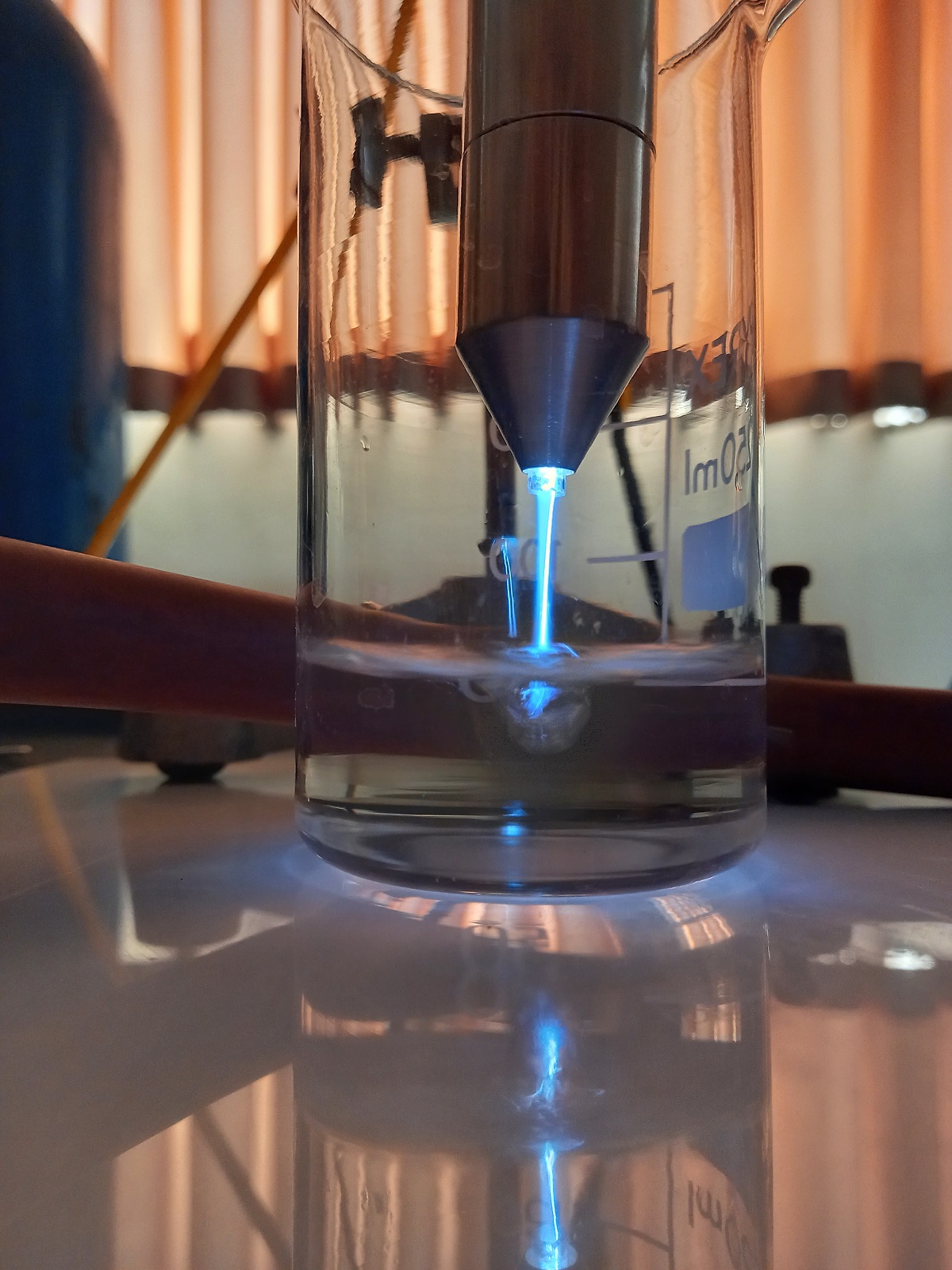
2. Helium atmospheric plasma jet
This plasma is a cold plasma that can be easily touched by hand. This jet was designed and built in the laboratory, and its effect on healthy and cancerous cells, as well as the study of plasma parameters, is currently being studied during the master's and doctoral theses.

3. Inductively coupled plasma source
A: Inductively coupled plasma using a kHz power supply
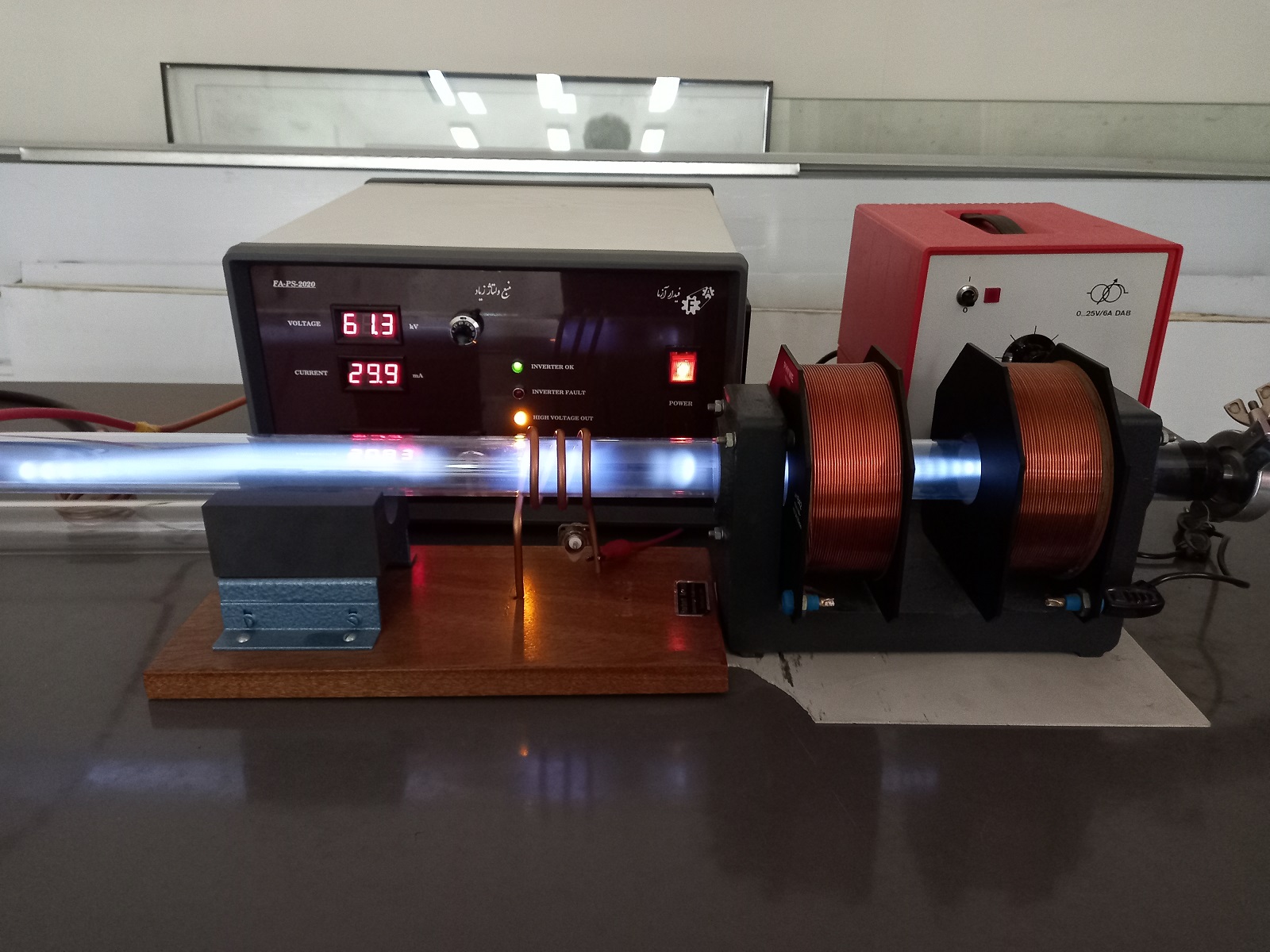

B: Inductively coupled plasma using a radio frequency power supply
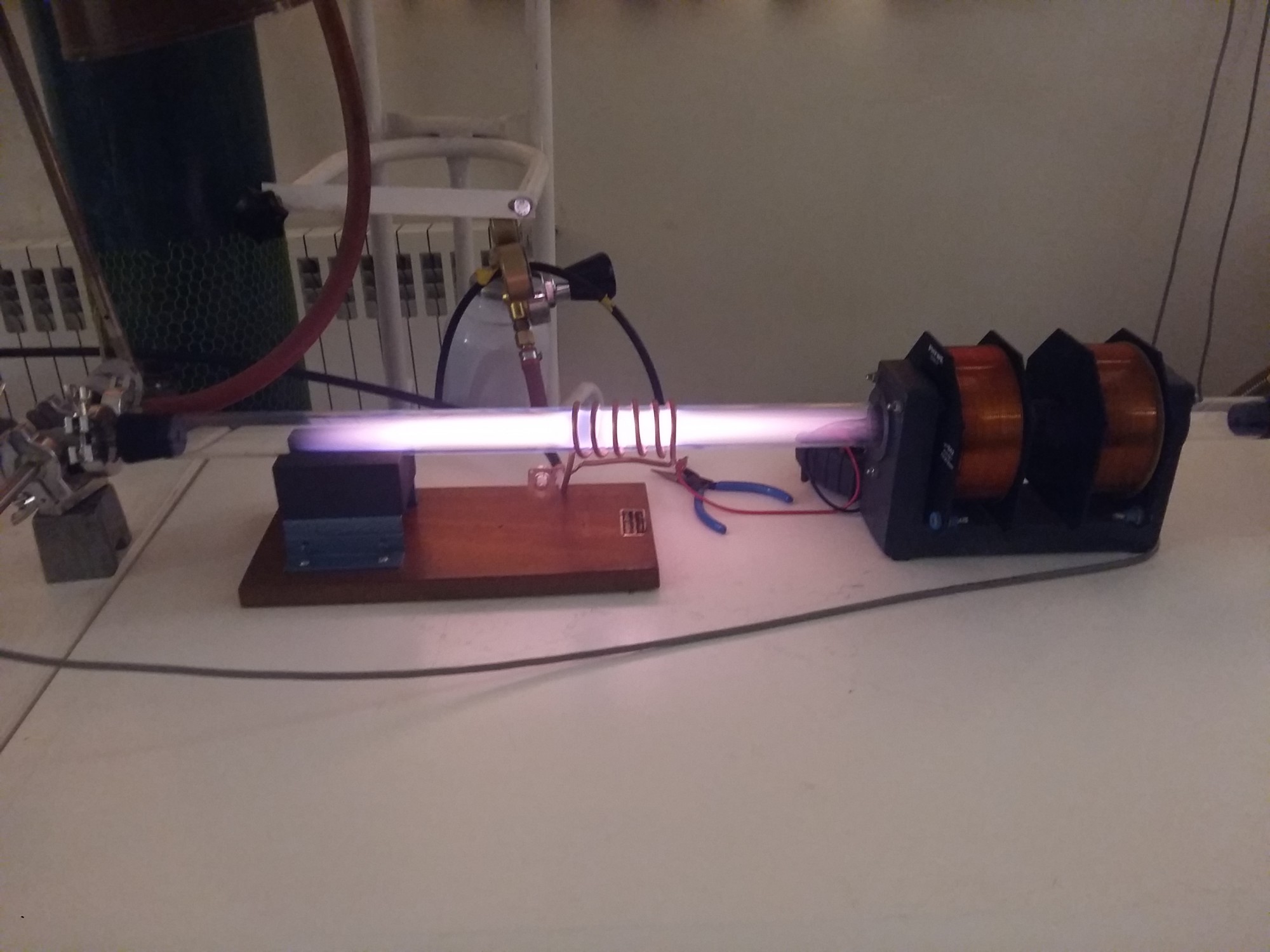
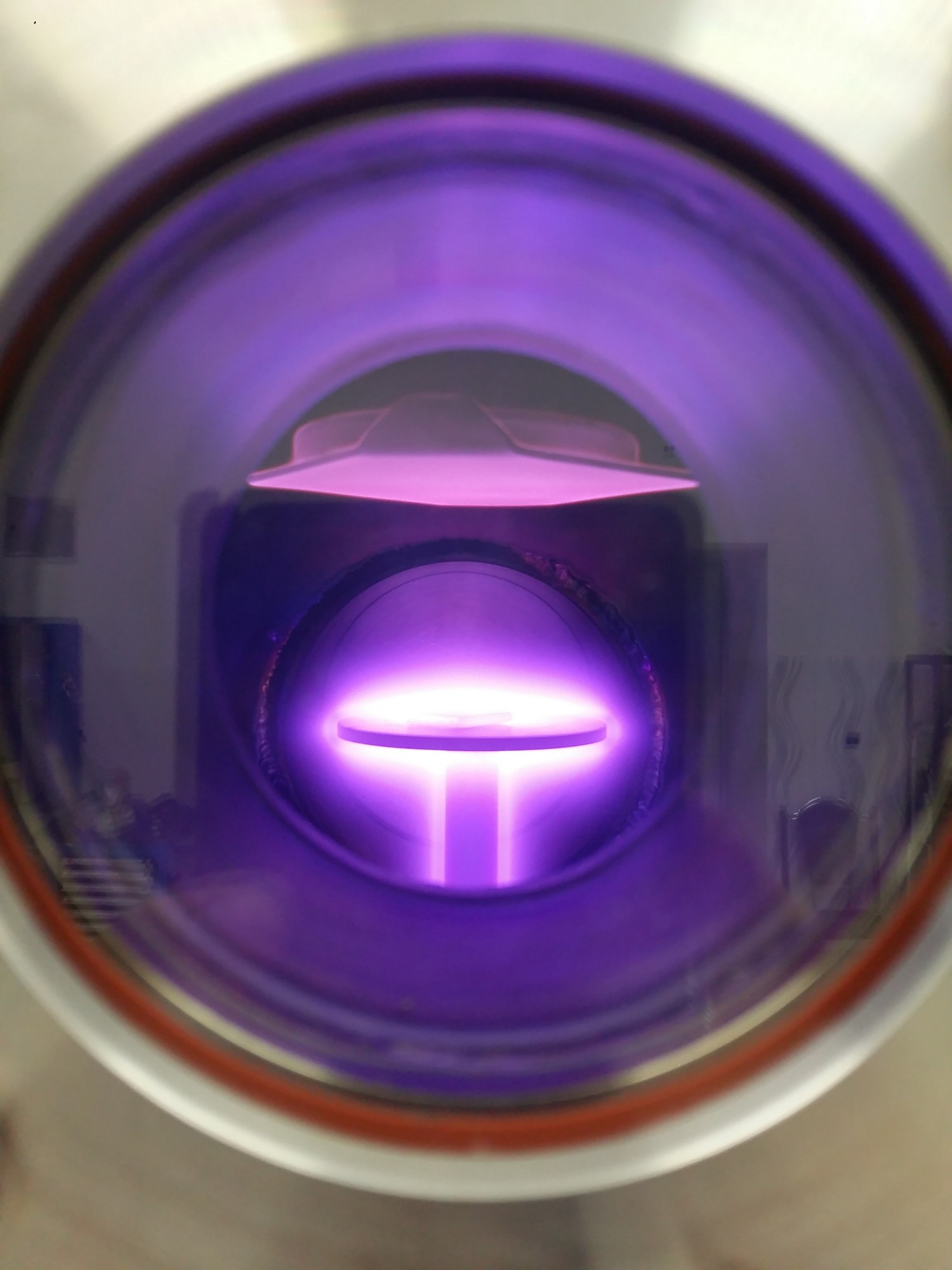
4. Nitration and plasma sputtering device
With the help of this device, metal layers can be created on glass, metal or ceramic materials, or by creating a nitride layer on the surface of metals, the resistance to corrosion or wear can be increased.


5. 5 kJ focal plasma device
.jpg)

6. Dielectric barrier discharge surface plasma
7. Direct current plasma
.jpg)


